AWS: 7 Powerful Reasons Why It Dominates Cloud Computing
In the fast-evolving world of cloud computing, one name stands out with unmatched dominance: AWS. With over 30% of the global cloud market, Amazon Web Services isn’t just leading—it’s redefining how businesses scale, innovate, and secure their digital futures.
What Is AWS and Why It Matters in Today’s Digital Landscape

Amazon Web Services, commonly known as AWS, is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. Launched in 2006, AWS offers over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally, serving millions of customers—including startups, enterprises, and government agencies.
The Origins of AWS: From Internal Tool to Global Powerhouse
AWS began as an internal solution to streamline Amazon’s own infrastructure. As Amazon scaled its e-commerce operations, it faced challenges in managing server capacity, deployment speed, and cost efficiency. Engineers realized that the tools they built could be offered as standalone services to other developers and businesses.
In 2006, AWS launched its first public services: Simple Storage Service (S3) and Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). These two foundational services allowed developers to store data and rent computing power on-demand—revolutionizing how applications were built and deployed.
According to AWS’s official history, this marked the birth of modern cloud computing. What started as a side project quickly became Amazon’s most profitable segment, contributing significantly to its overall revenue.
Core Components That Define AWS Architecture
AWS operates on a modular architecture where each service addresses a specific need. The core components include compute, storage, networking, databases, security, and machine learning. These services are designed to work together seamlessly while allowing independent scalability.
- Compute: Services like EC2, Lambda, and ECS enable flexible processing power.
- Storage: S3, EBS, and Glacier provide scalable, durable, and cost-effective storage solutions.
- Networking: VPC, Route 53, and CloudFront ensure secure and fast connectivity.
- Databases: RDS, DynamoDB, and Redshift support relational, NoSQL, and data warehousing needs.
“AWS gives you the building blocks to create virtually any type of application in the cloud.” — Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon and former AWS CEO
Key AWS Services That Power Modern Businesses
AWS isn’t just about offering services—it’s about enabling innovation. Let’s explore some of the most impactful AWS services that have become industry standards.
Amazon EC2: The Backbone of Cloud Computing
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is arguably the most iconic AWS service. It provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing businesses to launch virtual servers—called instances—within minutes.
EC2 supports a wide range of instance types optimized for different workloads: general-purpose, compute-optimized, memory-intensive, GPU-powered, and more. This flexibility makes it ideal for everything from web hosting to high-performance computing.
One of EC2’s biggest advantages is its pay-as-you-go pricing model. You only pay for the compute time you use, which eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware. For startups and small businesses, this lowers the barrier to entry for launching scalable applications.
Amazon S3: Scalable Object Storage for the World
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a cornerstone of AWS’s storage offerings. It provides industry-leading durability, availability, and performance for storing and retrieving any amount of data at any time.
S3 is used for a variety of use cases, including backup and restore, data lakes, static website hosting, and big data analytics. Its object-based storage model allows for easy organization using buckets and keys, while features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication enhance data management.
According to AWS, S3 is designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability, meaning your data is extremely unlikely to be lost. This level of reliability has made S3 the go-to storage solution for companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and NASA.
AWS Lambda: Serverless Computing Redefined
Lambda represents a paradigm shift in how developers think about infrastructure. Instead of managing servers, developers upload code that runs in response to events—such as an HTTP request, file upload, or database change.
With AWS Lambda, you don’t provision or manage servers. The service automatically scales your application by running code in response to each trigger. You’re charged only for the compute time consumed—down to the nearest millisecond.
This serverless model reduces operational overhead and allows teams to focus on writing business logic rather than managing infrastructure. Popular use cases include real-time file processing, chatbots, and backend APIs.
Global Infrastructure: How AWS Powers the Internet
AWS’s global infrastructure is one of its most significant competitive advantages. It enables low-latency access, high availability, and compliance with regional data regulations.
Regions, Availability Zones, and Edge Locations
AWS operates in geographically dispersed regions, each containing multiple Availability Zones (AZs). An AZ is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity. This design ensures fault tolerance and high availability.
As of 2024, AWS has 33 regions and 105 Availability Zones, with plans to expand into new markets like Saudi Arabia, Israel, and New Zealand. Each region is isolated from others to prevent cascading failures, yet connected via high-speed global networks.
In addition to regions and AZs, AWS uses Edge Locations—smaller data centers that power services like CloudFront (its content delivery network). These locations cache content closer to end users, reducing latency and improving performance.
Security and Compliance Across the AWS Global Network
Security is built into every layer of AWS’s infrastructure. The company follows a shared responsibility model: AWS secures the infrastructure, while customers secure their data and applications.
AWS complies with over 140 security standards and certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, GDPR, and FedRAMP. This makes it suitable for highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Additionally, AWS offers tools like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS Shield for DDoS protection, and AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) to help customers protect their environments.
Cost Management and Pricing Models in AWS
One of the biggest concerns for organizations adopting AWS is cost control. While the cloud offers flexibility, unmanaged usage can lead to unexpected bills. Understanding AWS’s pricing models is crucial for optimizing spend.
On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot Instances Explained
AWS offers several pricing options for EC2 instances:
- On-Demand Instances: Pay for compute capacity by the hour or second with no long-term commitments. Ideal for unpredictable workloads.
- Reserved Instances: Commit to using instances for 1 or 3 years in exchange for significant discounts—up to 75% off On-Demand prices.
- Spot Instances: Bid on unused EC2 capacity at steep discounts (up to 90% off). Best for fault-tolerant, flexible workloads like batch processing or CI/CD pipelines.
Choosing the right model depends on your workload’s predictability and tolerance for interruption.
Tools for Monitoring and Optimizing AWS Costs
AWS provides several tools to help you track and manage your spending:
- AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize and analyze your cost and usage patterns over time.
- AWS Budgets: Set custom cost and usage budgets to receive alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
- AWS Trusted Advisor: Offers real-time guidance to optimize cost, performance, and security.
- AWS Cost and Usage Report (CUR): Detailed reports that can be analyzed using tools like Amazon Athena or QuickSight.
Many organizations also use third-party tools like CloudHealth by VMware or Spot.io to gain deeper insights and automate cost optimization.
Security and Compliance: How AWS Protects Your Data
Security is not an afterthought in AWS—it’s a foundational principle. AWS implements a defense-in-depth strategy that spans physical data centers, network infrastructure, and application layers.
Shared Responsibility Model: Who Is Responsible for What?
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model clearly defines the division of security responsibilities:
- AWS is responsible for: The security of the cloud, including hardware, software, networking, and facilities.
- Customers are responsible for: Security in the cloud, including data encryption, identity management, firewall configuration, and OS patching.
This model empowers customers to maintain control over their security posture while relying on AWS’s robust infrastructure.
Key Security Services Offered by AWS
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of security services:
- AWS IAM: Enables fine-grained access control to AWS resources. You can define who can access what, under which conditions.
- AWS KMS (Key Management Service): Helps create and manage cryptographic keys for data encryption.
- AWS Shield: Protects against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
- AWS WAF: Filters malicious web traffic before it reaches your applications.
- AWS GuardDuty: Intelligent threat detection that continuously monitors for malicious activity.
- AWS Security Hub: Centralizes security alerts and compliance checks across multiple AWS accounts.
These tools, combined with AWS’s global compliance framework, make it one of the most trusted platforms for securing sensitive data.
Innovation and Emerging Technologies in AWS
AWS continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in cloud computing. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, AWS is investing heavily in next-generation technologies.
AWS AI and Machine Learning Services
AWS offers a broad set of AI and ML services that make it easier for developers to build intelligent applications without deep expertise in data science.
- Amazon SageMaker: A fully managed service that enables developers to build, train, and deploy machine learning models quickly.
- Amazon Rekognition: Image and video analysis service that detects objects, people, text, and activities.
- Amazon Polly: Text-to-speech service that turns written text into lifelike speech.
- Amazon Lex: Powers conversational interfaces like chatbots using the same technology as Alexa.
- Amazon Comprehend: Natural language processing (NLP) service that extracts insights from text.
These services are used by companies to automate customer support, analyze social media sentiment, enhance accessibility, and more.
IoT and Edge Computing with AWS
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries from manufacturing to healthcare. AWS IoT Core allows devices to securely connect to the cloud and exchange data with other AWS services.
With AWS Greengrass, you can run local compute, messaging, and data caching on devices even when they’re offline. This enables real-time decision-making at the edge—critical for applications like autonomous vehicles or industrial automation.
AWS also supports large-scale device management, secure communications, and over-the-air updates, making it a complete platform for building IoT solutions.
Quantum Computing with Amazon Braket
Amazon Braket is AWS’s quantum computing service. It provides a development environment to explore and experiment with quantum algorithms using simulators and actual quantum hardware from partners like IonQ, Rigetti, and Oxford Quantum Circuits.
While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems in cryptography, drug discovery, and logistics that are beyond the reach of classical computers. AWS is positioning itself as a leader in making this technology accessible to researchers and developers.
Migration Strategies: Moving to AWS Successfully
Migrating to AWS can be a complex undertaking, but with the right strategy, it can yield significant benefits in agility, cost savings, and innovation.
The 6R Framework for AWS Migration
AWS recommends the 6R framework to categorize migration approaches:
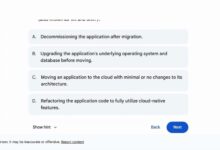
- Rehost (Lift and Shift): Move applications to the cloud without changes. Fastest but may not optimize cloud benefits.
- Refactor (Re-architect): Modify applications to take advantage of cloud-native features like auto-scaling and serverless.
- Rearchitect: Redesign applications using microservices and containers for better scalability.
- Replatform: Make minor optimizations, such as moving to a managed database service.
- Repurchase: Switch to a different product, often a SaaS solution.
- Retire: Decommission applications that are no longer needed.
Most organizations use a combination of these strategies depending on the application’s complexity and business value.
Tools and Services That Facilitate AWS Migration
AWS provides several tools to streamline migration:
- AWS Migration Hub: Tracks the progress of migration projects across multiple tools and services.
- Server Migration Service (SMS): Automates the replication of on-premises servers to AWS.
- Database Migration Service (DMS): Migrates databases with minimal downtime.
- AWS Snow Family: Physical devices (Snowcone, Snowball, Snowmobile) for transferring large datasets securely.
- Application Discovery Service: Helps identify on-premises assets and their dependencies.
These tools reduce risk, accelerate timelines, and provide visibility throughout the migration lifecycle.
Training, Certification, and Community Support for AWS
AWS invests heavily in education and workforce development. Its training and certification programs are among the most respected in the IT industry.
AWS Certification Paths and Their Value
AWS offers a tiered certification program that validates technical expertise:
- Foundational: AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner – ideal for non-technical roles.
- Associate: Includes Solutions Architect, Developer, and SysOps Administrator.
- Professional: Advanced certifications for architects and DevOps engineers.
- Specialty: Focused on areas like security, machine learning, databases, and advanced networking.
Earning an AWS certification can boost your career, increase earning potential, and demonstrate credibility to employers. According to AWS’s certification page, certified professionals are in high demand across industries.
Community and Developer Resources
AWS has a vibrant global community of developers, partners, and users. Resources include:
- AWS Developer Forums: Active discussion boards for troubleshooting and best practices.
- AWS Blogs and Whitepapers: In-depth technical content from AWS experts.
- AWS re:Invent: Annual conference featuring keynote announcements, workshops, and networking.
- AWS Open Source Projects: GitHub repositories with tools and frameworks.
- AWS Educate: Program for students and educators to learn cloud skills.
These resources empower users to stay updated, solve problems, and innovate using AWS.
What is AWS and why is it important?
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the world’s leading cloud computing platform, offering over 200 services including computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and security. It’s important because it enables businesses to scale rapidly, reduce IT costs, and innovate faster without managing physical infrastructure.
How does AWS pricing work?
AWS uses a pay-as-you-go model with no upfront costs. You pay only for the services you use. Pricing varies by service and includes options like On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot Instances for compute. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer help monitor and optimize spending.
Is AWS secure?
Yes, AWS is highly secure. It follows a shared responsibility model—AWS secures the infrastructure, and customers secure their data. AWS complies with global security standards and offers services like IAM, KMS, Shield, and WAF to enhance security.
What are the most popular AWS services?
The most popular AWS services include Amazon EC2 (compute), S3 (storage), Lambda (serverless), RDS (databases), CloudFront (CDN), and IAM (security). These services form the backbone of most cloud architectures.
How can I get certified in AWS?
You can get AWS certified by choosing a certification path (Cloud Practitioner, Associate, Professional, or Specialty), preparing with AWS training materials, and passing the exam. Exams are administered through Pearson VUE or online proctoring.
In conclusion, AWS has redefined the landscape of cloud computing by offering a powerful, scalable, and secure platform that meets the needs of businesses of all sizes. From its foundational services like EC2 and S3 to cutting-edge innovations in AI, IoT, and quantum computing, AWS continues to lead the industry. With robust global infrastructure, comprehensive security measures, and a strong commitment to training and support, AWS empowers organizations to innovate faster and operate more efficiently. Whether you’re a startup or a Fortune 500 company, understanding and leveraging AWS can be a game-changer for your digital transformation journey.
Further Reading: